
Sina Wittayawiroj’s exhibition Can’t We Recant? (เราจะถอนคำพูดไม่ได้เลยหรือ?) opens at the MAIELIE gallery in Khon Kaen on 20th March, and runs until 7th June. The exhibition explores Sina’s personal and artistic background, and his connection to the major political events of his lifetime. It was first shown last year at Kinjai Contemporary in Bangkok.


One section, which deals with the 2010 red-shirt crackdown, is titled The Awakening, situating Sina within the “Post-Ratchaprasong art” movement, a label coined by the journal Read (อ่าน; vol. 3, no. 2) describing artists whose work took on a political dimension in response to the crackdown. Sina is one of a generation of artists, writers, and filmmakers who experienced a political awakening in 2010, including Prakit Kobkijwattana, Veeraporn Nitiprapha, Uthis Haemamool, and Chulayarnnon Siriphol. Political awakening is known in Thai as ta sawang, and Chulayarnnon — along with five other directors — discussed his ta sawang experience in an interview for Thai Cinema Uncensored.
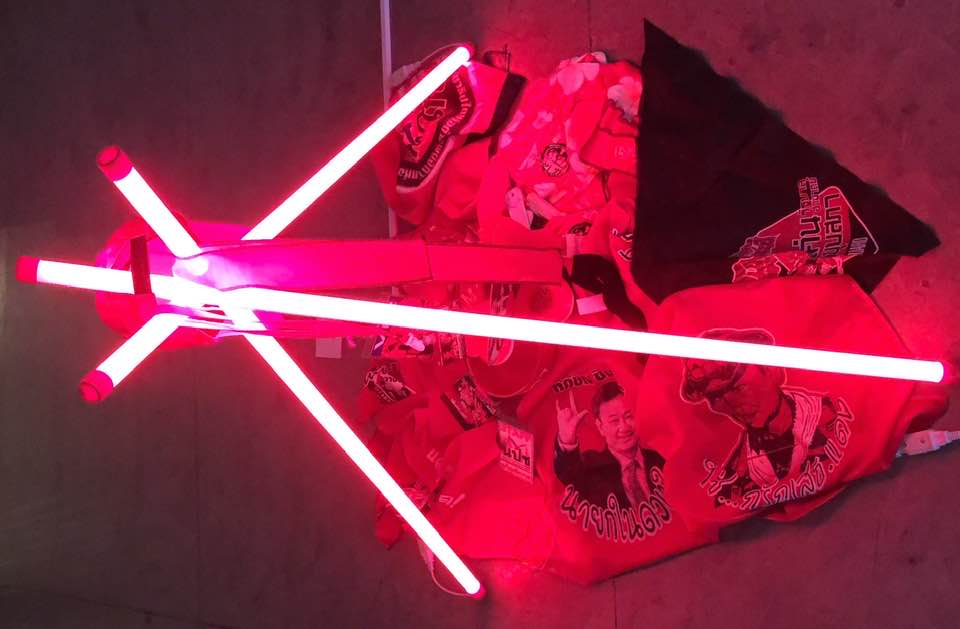

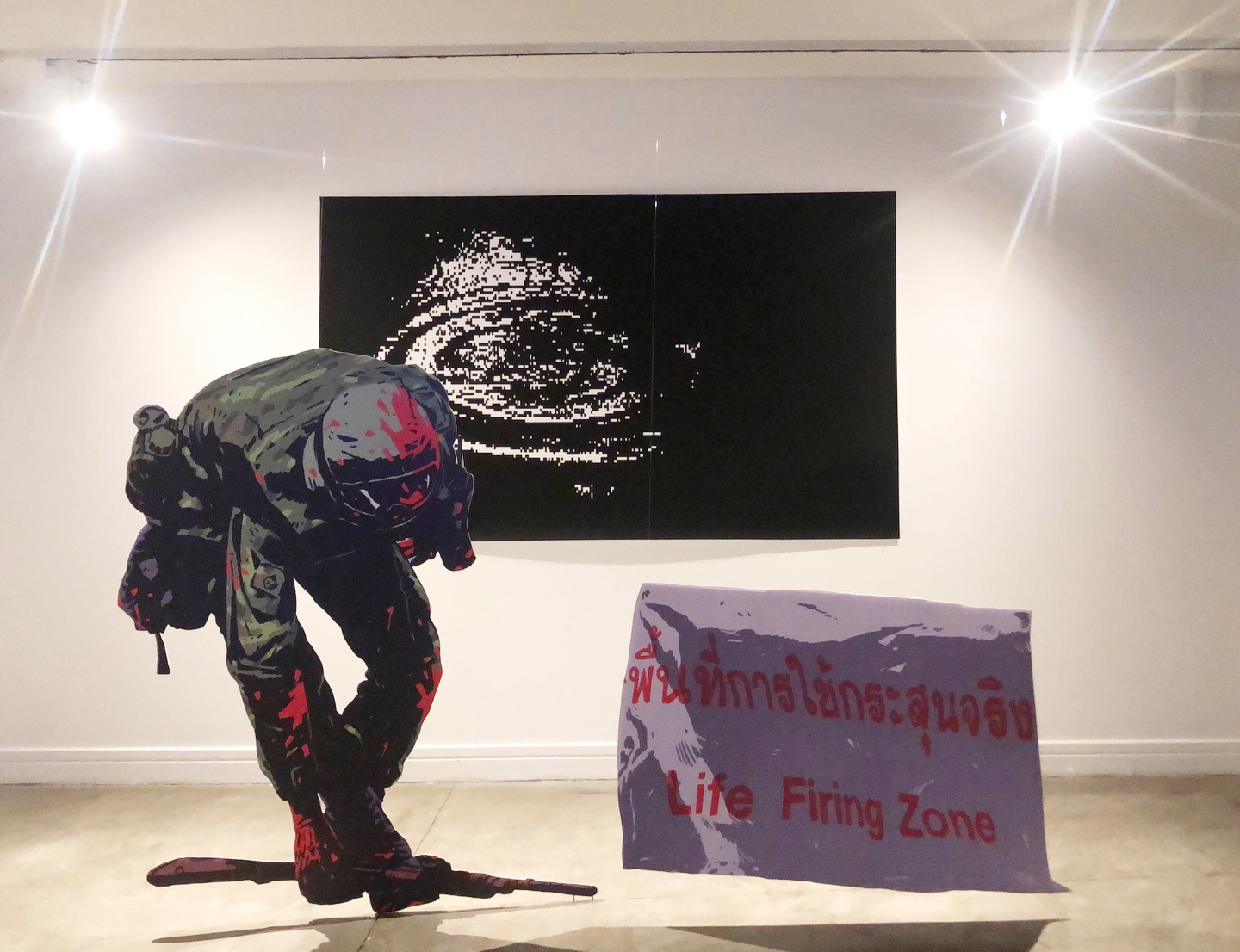
The Awakening features two installations. One is a life-sized recreation of a famous photograph from 15th May 2010, showing a soldier next to a sign warning that live ammunition was used against the red-shirts. (Red splotches have been added to the soldier’s uniform, as a reminder that the sign was accurate.) The other is a pile of red-shirt memorabilia (such as handclappers and clothing), under a neon pyramid.

Your Ash and My Bone
Sina’s film Your Ash and My Bone (ธุลีดาว) is also screening throughout the exhibition. Your Ash and My Bone is a documentary collage film in which the artist narrates his life story from birth to the present, from his family background to the progress of his artistic career.
The autobiographical narration is juxtaposed with an account of Thailand’s political turmoil over the same period. There is archive footage of Black May, the 2006 coup (which Sina describes as “this poisonous tree attempting to root itself deepest into society”), the red-shirt crackdown, the whistle-blower protests, the 2014 coup, and the student protest movement of 2020–2021.
The autobiographical narration is juxtaposed with an account of Thailand’s political turmoil over the same period. There is archive footage of Black May, the 2006 coup (which Sina describes as “this poisonous tree attempting to root itself deepest into society”), the red-shirt crackdown, the whistle-blower protests, the 2014 coup, and the student protest movement of 2020–2021.

Coloured filters are used to add political commentary to some of the events: blue for 2006, red for 2010, and yellow for 2014. Music is also a key element: a montage of scenes showing the arrest of Arnon Nampa and water cannon being used in Siam Square is accompanied by Caravan’s song Jit Phumisak (จิตร ภูมิศักดิ์), linking today’s student protesters to the revolutionary young writer who was killed in 1966.

Your Ash and My Bone also highlights some of Thailand’s artistic controversies over the past two decades: the banning of Apichatpong Weerasethakul’s Syndromes and a Century (แสงศตวรรษ), protests against Anupong Chantorn’s painting Perceptless (ภิกษุสันดานกา), and the censorship of the Rupture (หมายเหตุ ๕/๒๕๕๓) exhibition. The film shows how political repression and artistic censorship are equally corrosive.
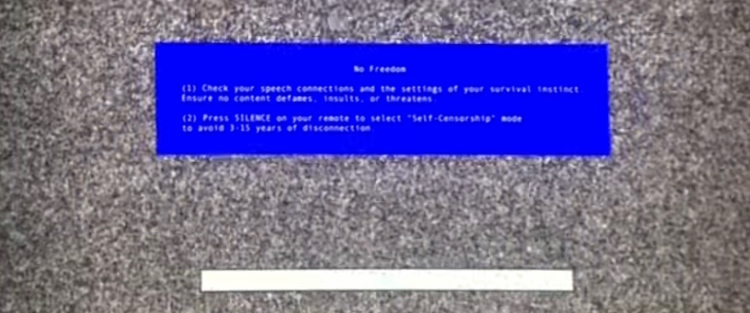
Some self-censorship was necessary, and Sina draws attention to this by periodically displaying a spoof computer error screen (“No Freedom”) and obscuring certain words in the English subtitles. Abhichon Rattanabhayon used a similar tactic in his short film The Six Principles (สัญญาของผู้มาก่อนกาล), as did Pen-ek Ratanaruang in Paradoxocracy (ประชาธิป'ไทย).





















